[Theory] Queue
23 Feb 2022큐(Queue)
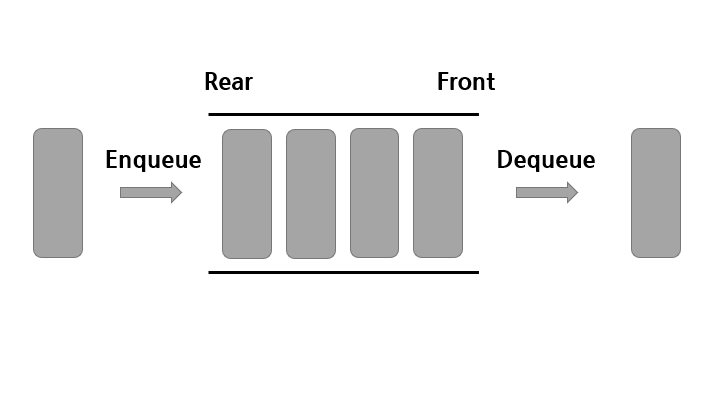
선입선출(First In First Out)의 특성을 가지는 자료구조로 Stack과 반대의 개념을 가진다. 한 쪽 끝에서는 자료의 삽입연산만 가능하고 반대쪽 끝에서는 삭제만 가능한 구조이다.
큐의 연산종류
- Enqueue : 큐의 가장 마지막에 데이터를 추가합니다. (입력연산)
- Dequeue : 큐의 가장 맨 앞 데이터를 삭제하고 반환한다. (출력연산)
- Peek : 큐가 비어있지 않을 경우 맨 앞 데이터를 반환한다. (조회연산)
시간의 시간복잡도
큐 데이터를 삽입하거나 제거시 삽입의 경우 Front에서만 일어나고 제거의 경우 Rear에서만 일어난다. 그러므로 삽입과 삭제에 소요되는 시간복잡도는 O(1)이다. 조회는 특정 데이터를 찾을 때까지 수행해야 하므로O(n)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
큐의 구헌
Java에서는 Stack과 동일하게 Collection 클래스로 구현 되어있다.
QueueNode
Queue의 노드객체
QueueList
Queue의 연산클래스